Mechanisms and Logic in Human Physiology
This channel is all about helping students of human physiology gain true understanding of physiological function so they can stop relying so heavily on memorization. Learn the logic of physiology and your application of knowledge skills will dramatically improve (along with your exam scores!). As Einstein once said, "Any fool can know. The point is to understand."

Figure 4.25. The liver is a metabolic hub

Figure 4.21. Stress effects on metabolism

Figure 4.15. The Cori cycle

Figure 4.9. Pacemaker enzymes and metabolic control

Figure 4.6. Reversible chemical reaction dynamics

Figure 4.4. Enzyme catalytic cycle default

Figure 4.1. Catabolism and anabolism

Figure 3.25. Epithelial transport

Figure 3.24. Gated channels
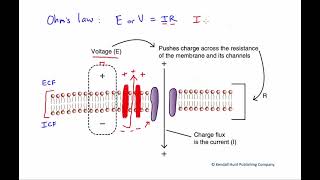
Figure 3.18. Ohm's law

Figure 3.14. Carrier protein transport rates
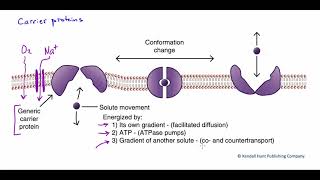
Figure 3.13. Carrier proteins

Figure 3.6. Cell membrane proteins

Figure 3.5. Fluid compartment barriers

Figure 3.3. Fluid compartments

Figure 3.2. Glycocalyx and an ECF hydrogel

Figure 3.1. Water structure

Figure 2.22. Cell-cell junctions
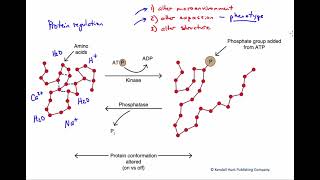
Figure 2.21. Protein regulation

Figure 2.19. Protein substrate interactions

Figure 2.18. Protein structure

Figure 2.9. Membrane structure

Figure 2.6. Hydrogen bonds

Figure 2.4. Ionic bonding and ionization

Figure 2.3. The structure of water

Figure 1.5. Limitations of diffusion

Fig 1.4. Protein structure function

Withdrawal and crossed extensor reflexes

The reflex arc

Synapses