Dale Button
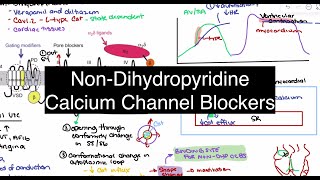
How Verapamil and Diltiazem Work 🫀 Non-DHP Calcium Channel Blockers Explained

Amlodipine and Dihydropyridines 🧬 How They Work Differently from Verapamil

L-Type Calcium Channels Explained: Cav1.2, Cardiac Contraction, and Calcium Channel Blockers 💥

Class Ic Antiarrhythmics Explained: Why Flecainide Hits Hard and Stays Bound

Why Lidocaine Targets Ischemic Tissue: Inactivation, APD, and Membrane Stability

Class 1A Antiarrhythmics: How They Block Sodium and Potassium Channel

Lidocaine and Class 1B Antiarrhythmics: Mechanism of Action in the Ischemic Tissue

Nav1.5 Sodium Channel Explained: Activation, Inactivation, and Deactivation

Understanding Mobitz Type II (Second-Degree Heart Block) – ECG Analysis & Pathophysiology

How Ischemia Causes Mobitz Type I (Second-Degree AV Block) | ECG Analysis & Pathophysiology

Understanding Mobitz Type I (Second-Degree Type 1 AV Block) – ECG Breakdown & Pathophysiology

Hyperkalemia Explained: Identifying Shockable Rhythms in Dialysis Patients

Hyperkalemia Explained: When to Shock and When to Wait

Hyperkalemia Explained: Pathophysiology of Sine Waves

Hyperkalemia Explained: Pathophysiology of Peaked T-Waves

REVERT Procedure for SVT: The Science Behind the Modified Valsalva Maneuver

Why Hypoxia Causes Bradycardia in Pediatric Patients: The Cardiac & Autonomic Impact Explained

How Hypoxic Vasoconstriction Leads to Pulmonary Hypertension: A Deep Dive into Causes and Effects

How Calcium Gluconate Stabilizes Heart Cells in Hyperkalemia

Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythms and Reperfusion

Acute Pain Management Strategies and Considerations

Opioid Mechanism of Action

Acetaminophen and NSAID Mechanism of Action for Analgesia

Stroke Assessment and Los Angeles Motor Score LAMS Pathophysiology

Pathophysiology and Treatment of COPD

Left Bundle Branch Block Electrophysiology

J-Point Recognition

Ischemic T-Wave Inversion

High Yield Assessment for Cardiac Ischemia

Oxytocin Pharmacology and Role in Postpartum Hemorrhage