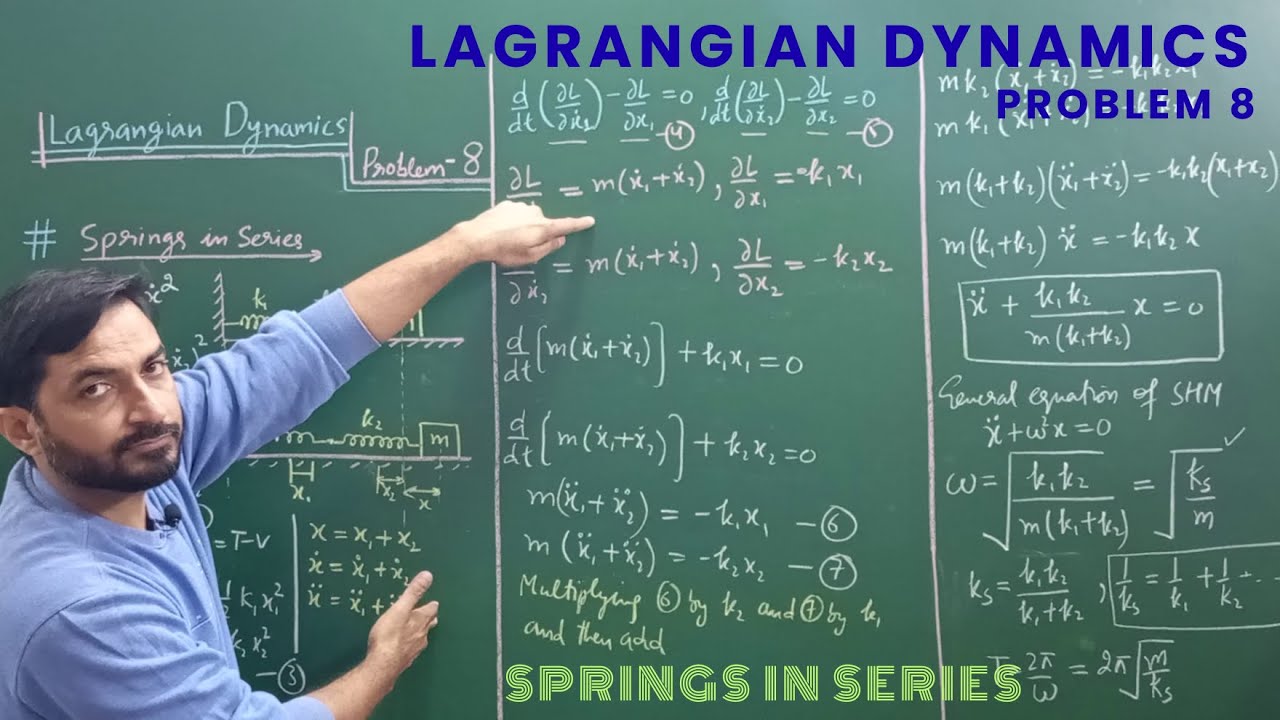
Lagrangian Dynamics - Problem 8 - Mass attached to springs in series, on a horizontal plane
Автор: Hologram
Загружено: 2025-12-03
Просмотров: 52
Lagrangian Dynamics – Problem 8
Analysis of Motion of a Mass Attached to Two Springs in Series on a Horizontal Plane using Lagrangian Mechanics
In this video, we dive into the Lagrangian analysis of a system where a mass is connected to two springs in series and placed on a horizontal plane. This setup introduces interesting dynamics due to the effective spring constant and the constraints of motion, making it a rich example for applying analytical mechanics.
🔍 What you’ll learn in this video:
• How to model a two-spring system in series on a horizontal plane
• Step-by-step derivation using Lagrangian mechanics
• The role of the effective spring constant in simplifying the system
• How constraints are applied to describe the motion of the mass
• The resulting equation of motion and its physical interpretation.
How to choose generalized coordinates
Express kinetic (T) and potential (V) energy in terms of x,x ̇
Build the Lagrangian: L=T-V
Derive the equation of motion using Euler-Lagrange
________________________________________
🌊 🌟 Advantages of Lagrangian Mechanics over Newtonian dynamics
• Generalized Coordinates: Uses any convenient coordinates (not just Cartesian), simplifying complex systems like rotational or constrained motion.
• Energy-Based: Formulated using kinetic and potential energy, avoiding direct force calculations, which is ideal for systems with many forces.
• Handles Constraints Easily: Naturally incorporates constraints (e.g., springs, pendulums) via generalized coordinates, reducing equations to solve.
• Symmetry and Conservation: Directly reveals conservation laws (e.g., energy, momentum) through symmetries, unlike Newtonian’s force-based approach.
• Scalable to Complex Systems: Simplifies analysis of multi-body or non-rigid systems, like coupled oscillators or relativistic dynamics.
________________________________________
🛠️ Prerequisites
Basic calculus (derivatives, chain rule)
High school physics (velocity, acceleration, energy)
No forces, no torques, no free-body diagrams needed!
________________________________________
📚 Resources & Further Reading
Goldstein’s Classical Mechanics (Ch. 1–2)
Feynman Lectures, Vol. I, Ch. 19
Classical Mechanics by J C Upadhyaya
________________________________________
📱Connect with Me for More Physics Fun:
Telegram: Join my physics community for exclusive resources, discussions, and updates! – https://t.me/Hologram2dd
Instagram: Follow for bite-sized physics tips, behind-the-scenes content, and more! https://www.instagram.com/hologram.2d...
Facebook: Stay connected with my physics community and get the latest updates! / 1mtykkbndu
___________________________________________________________________
Lagrangian Mechanics Problem 1 - • Lagrangian Mechanics - (Problem 1) - Motio...
Lagrangian Mechanics Problem 2 - • Lagrangian Mechanics - (Problem 2) - Newto...
Lagrangian Mechanics Problem 3 - • Lagrangian Mechanics - (Problem 3) - Motio...
Lagrangian Mechanics Problem 4 - • Lagrangian Mechanics - ( Problem 4 ) - Mot...
Lagrangian Mechanics Problem 5 - • Lagrangian Dynamics - Problem 5 - Compound...
Lagrangian Mechanics Problem 6 - • Lagrangian Dynamics - Problem 6 - Atwood M...
Lagrangian Mechanics Problem 7 - • Lagrangian Dynamics - Problem 7 - Atwood m...
Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке:



















