Magnetic Distance–Controlled LED Brightness
Автор: Electricum
Загружено: 2026-01-02
Просмотров: 159
Project Briefing
Magnetic Distance–Controlled LED Brightness
Arduino Nano + Analog Hall Effect Sensor
________________________________________
Project Overview
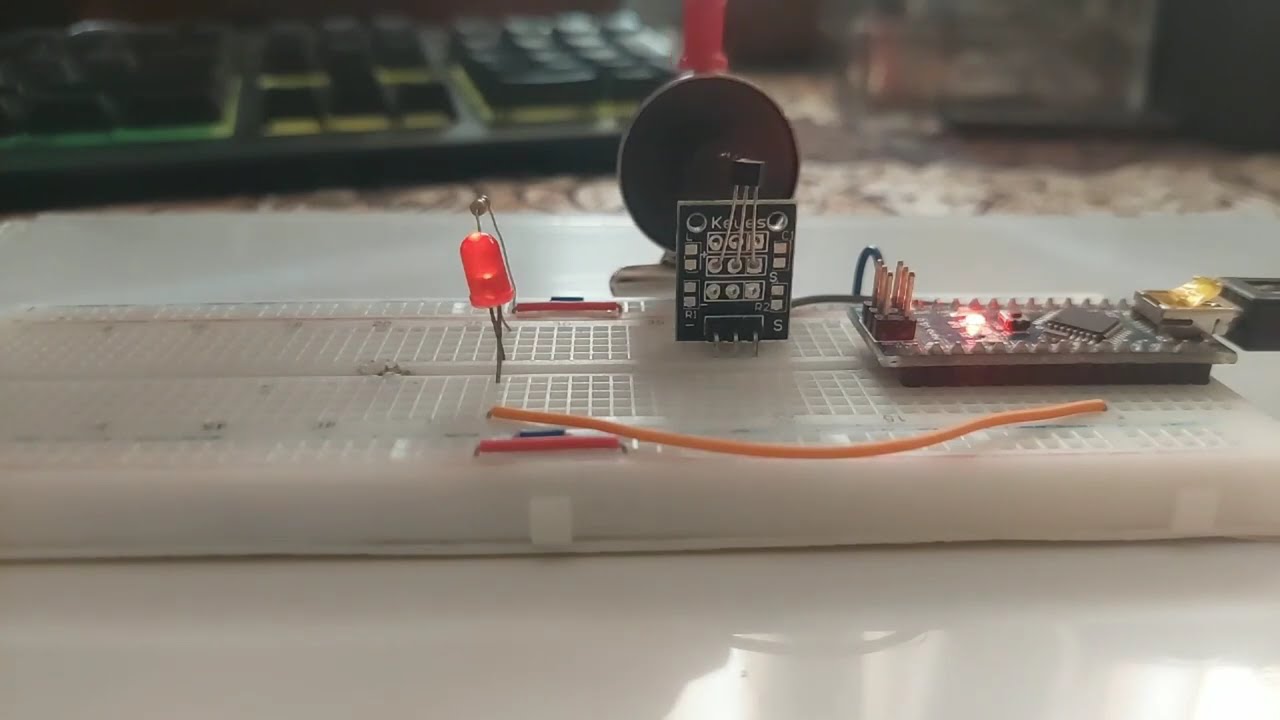
This project demonstrates how a magnetic field can be measured without physical contact and visualized using LED brightness. An analog Hall effect sensor detects the strength of a nearby magnet, and the Arduino Nano converts this signal into a PWM output that smoothly controls an LED.
As the magnet moves closer, the LED becomes brighter.
As the magnet moves away, the LED dims smoothly.
________________________________________
Components Used
• Arduino Nano
• Analog Hall effect sensor (e.g. SS49E, A1324, or KY-024 analog output)
• LED
• 220 Ω resistor
• Magnet (any small permanent magnet)
• Breadboard & jumper wires
________________________________________
How It Works
1. The Hall sensor outputs a voltage proportional to the magnetic field strength.
2. With no magnet present, the output is around 2.5 V (ADC ≈ 512).
3. As a magnet approaches, the voltage shifts up or down smoothly.
4. The Arduino reads this value on an analog input (A0).
5. The difference from the center value (512) represents magnetic strength.
6. This value is mapped to PWM (0–255).
7. The LED brightness changes smoothly using analogWrite().
________________________________________
Why Analog Hall Sensor Is Better
• Digital Hall sensors only output ON / OFF
• Analog Hall sensors provide continuous distance information
• Enables true proximity-based fading, not an illusion
• Ideal for smooth visualizations and control systems
https://github.com/ukkokalevala/Magne...
Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке:



















