How EPAP Works - Mechanisms Of Action
Автор: BMedical Pty Ltd
Загружено: 7 дек. 2011 г.
Просмотров: 19 242 просмотра
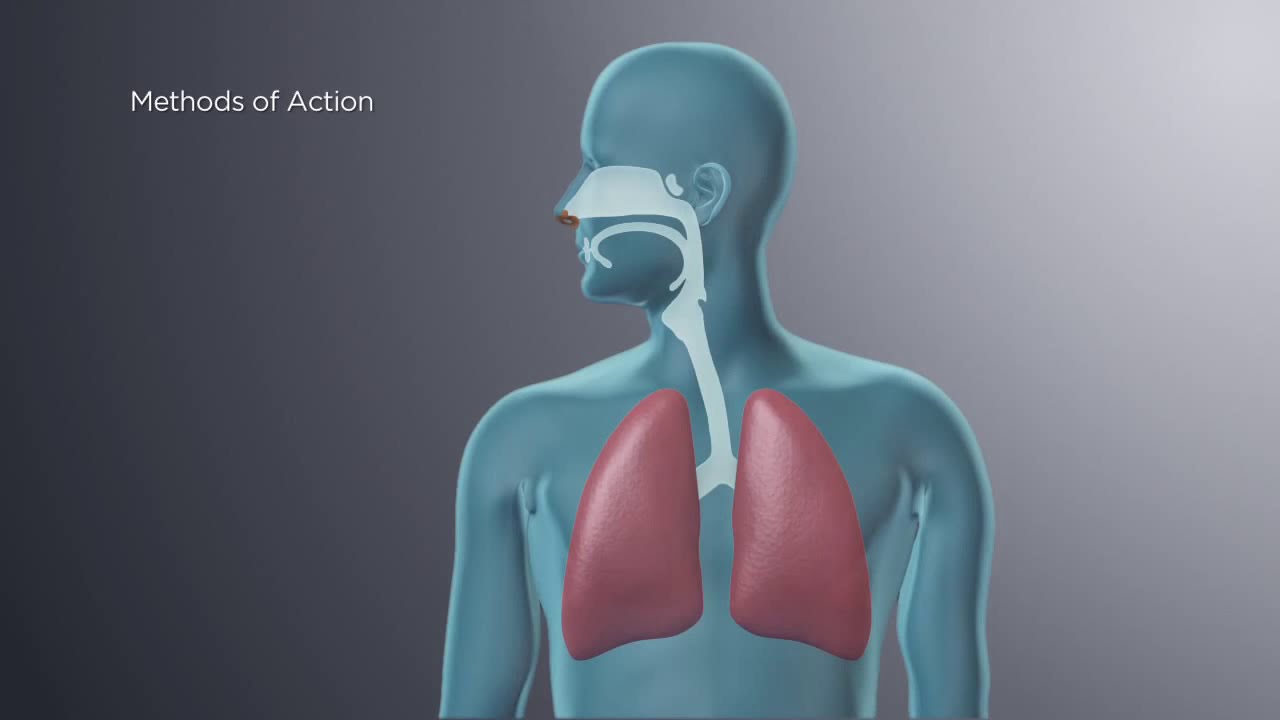
For the complaint patients, EPAP is very attractive as it requires no machine, tube or power supply. During inhalation, the patient inhales through their nose as normal. For many patients, Bongo and OptiPillow EPAP devices offer mild nasal dilation that will reduce inspiratory resistance. During exhalation, the valve closes and air passes through a narrow opening. This creates resistance to airflow, thus increasing the backpressure in the upper airways. There are 3 known mechanisms of action for EPAP:
1. The backpressure slows down exhalation and leads to pressure remaining in the airways at the end of the exhalation. This holds the airway wider than normal breathing.
2. This increased air in the lungs at the end of exhalation (FRC) causes a 'Tracheal Tug' reducing the susceptibility of the airways to collapse.
3. There is a slight CO2 increase. This improves muscle tone and respiratory drive.
However, this mechanism will vary for different patients. This is the best EPAP educational video created by Provent.
Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке:









