Igneous Rock | आग्नेय चट्टान | Indian Geography Animation | by Ravi Yadav (MNNIT Alumni)
Автор: Shri Adda
Загружено: 13 июн. 2024 г.
Просмотров: 18 367 просмотров
Download SHRI ADDA application https://play.google.com/store/apps/de...
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Igneous Rock | आग्नेय चट्टान | Indian Geography Animation | by Ravi Yadav (MNNIT Alumni)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sedimentary rocks UPSC, Igneous rocks examples, Types of igneous rocks UPSC, Metamorphic rocks UPSC, Intrusive igneous rocks, Extrusive igneous rocks, Types of rocks notes PDF, Types of rocks UPSC,
The earth’s crust is composed of rocks. A rock is an aggregate of one or more minerals. Rock may be hard or soft and in varied colors.
For example:
Granite is hard, soapstone is soft.
Gabbro is black and quartzite can be milky white.
Rocks do not have a definite composition of mineral constituents. Feldspar and quartz are the most common minerals found in rocks.
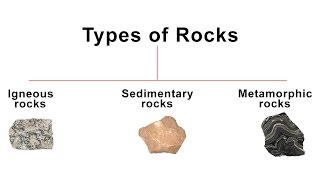
There are many different kinds of rocks which are grouped under three families on the basis of their mode of formation.
Igneous Rocks: Igneous rock is formed by the solidification of magma and lava. This is also known as the primary rock. Ex. Granite and Basalt etc.
Sedimentary Rocks: Sedimentary rocks are the result of deposition of fragments of rocks by exogenous processes. This is also known as the secondary rocks. Ex: sandstone, limestone, shale etc.
Metamorphic Rocks: Metamorphic Rocks formed from already-existing rocks that are undergoing recrystallization. Tertiary rocks are another name for metamorphic rocks. Ex: phyllite, schist, gneiss, quartzite and marble etc.
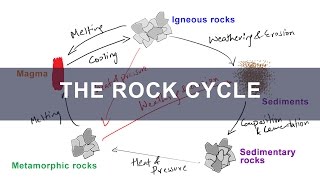
Igneous rocks form out of magma and lava from the interior of the earth, they are known as primary rocks.
The igneous rocks are formed when magma cools and solidifies. When magma in its upward movement cools and turns into solid form it is called igneous rock.
The process of cooling and solidification can happen in the earth’s crust or on the surface of the earth.
Igneous rocks are classified based on texture. Texture depends upon size and arrangement of grains or other physical conditions of the materials.
If molten material is cooled slowly at great depths, mineral grains may be very large.
Sudden cooling (at the surface) results in small and smooth grains.
Intermediate conditions of cooling would result in intermediate sizes of grains making up igneous rocks.
Granite, gabbro, pegmatite, basalt, volcanic breccia and tuff are some of the examples of igneous rocks.
The process of cooling and solidification can happen in the earth’s crust or on the surface of the earth.

Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке: