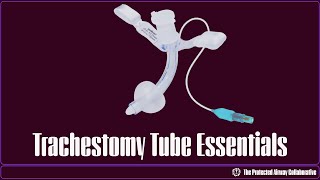
ACV - Above cuff vocalisation (National Tracheostomy Safety Project)
Автор: National Tracheostomy Safety Project
Загружено: 2017-11-07
Просмотров: 57214
For some patients, it is not possible to deflate the tracheostomy tube cuff. This is usually because high pressure ventilation is required or there is risk of ‘aspirating’ oral or gastric secretions or contents into the airway (the inflated cuff can offer some protection against this).
Above Cuff Vocalisation, or ACV, can help in these situations. This technique uses the subglottic suction port of specialised tracheostomy tubes to deliver a low flow of gas (air or oxygen) backwards, up the subglottic suction port, to exit above the cuff. This gas flow can then travel upwards through the trachea, pass through the vocal cords and exit via the mouth. This can result in audible vocalisation in around 80% of patients who would otherwise not be able to speak. ACV is particularly useful for those patients who cannot tolerate or be managed with a deflated tracheostomy tube cuff.
Guidelines for ACV are being developed as this is a relatively new technique. However, there are some principles to consider:
The NTSP does not recommend ACV unless this is performed by an appropriately trained member of healthcare staff, following a detailed risk assessment of the patient.
Contraindications include
Upper airway obstruction or concerns about the patency of the airway
An altered upper airway
A new tracheostomy (typically less than 72 hours old)
Any problems with the stoma, such as infection, bleeding or tissue breakdown
If continuous subglottic suction is required
A tracheostomy tube that is not in an optimal position
A patient that is too drowsy to cooperate and coordinate vocalisation efforts
The NTSP considers the following points to be good practice, based on our experience and what literature there is currently available.
Do not leave the patient un-attended during an ACV trial. We recommend limiting the trial to 15 minutes at a time, as there are concerns around drying the larynx with ACV air that are not yet fully understood.
Use a ‘thumb port’ (see video, or paper) so that there is only continuous gas flow when the port is actively occluded. This minimises the risk of a pressure build up should the ACV port become obstructed.
Monitor the patient continually
Stop the trial if there is any evidence of
Gas escaping via the stoma, alongside the tracheostomy tube
Pain or discomfort reported by the patient
No voice, or no evidence of gas passing via the upper airways
Swelling or surgical emphysema that develops at the site
The patient becomes fatigued
We recommend that subglottic and oral suction is performed prior to ACV. Warn the patient that they can expect some secretions to be ‘blown’ into their mouth. This can be unpleasant, require oral suction or lead to bad tastes or smells being experienced. Patients will frequently cough when commencing ACV as often the larynx has not been used for some time and can be sensitive.
Finally, the ACV gas flow is essentially continuous, throughout inspiration and expiration. This can take some getting used to. Our early work has demonstrated that ACV is safe and well tolerated and can lead to vocalisation in around 80% of patients in whom it is indicated. There may be additional benefits from promoting early trans-laryngeal gas flow that are currently not well understood.
ACV is an important option for patients who require tracheostomy cuff inflation and can lead to significant benefits from restoring the voice at these difficult times.

Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке: