Selenium automation testing course with Java-static and final keywords in java- class 13
Автор: Learn Java
Загружено: 2025-06-27
Просмотров: 116
You can learn Java with me as the Java Programming language is being made easily. It would take a period of minimum three months and maximum 6 months to master Java. I would recommend you to watch all my videos to crack any software interviews that would require Java Programming language as a primary skill.
class 13:
========
continued from class 12
3. Pass current object as a parameter
Useful when you need to pass the current object to a method or constructor.
public void display(Student s) {
System.out.println(s.name);
}
public void show() {
display(this); // passing current object
}
Return current object from a method
4. Allows method chaining.
======================
public class Student {
public Student getStudent() {
return this;
}
}
5. Access current class methods
===============================
Though implicit, you can use this to call methods within the same class.
public void show() {
this.display(); // same as display()
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Hello");
}
static context in java:-
==================
Static Context = Class-Level Context
When you declare something as static in Java, it is shared among all instances of that class and can be accessed without creating an object.
Examples of Static Context
======================
Static variables:
============
Static variables are recognized and executed at the time of loading the byte code to the memory.
class MyClass {
static int count = 0; // belongs to the class
}
Static methods:
class MyClass {
static void display() {
System.out.println("Static method");
}
}
MyClass.display(); // No need to create an object
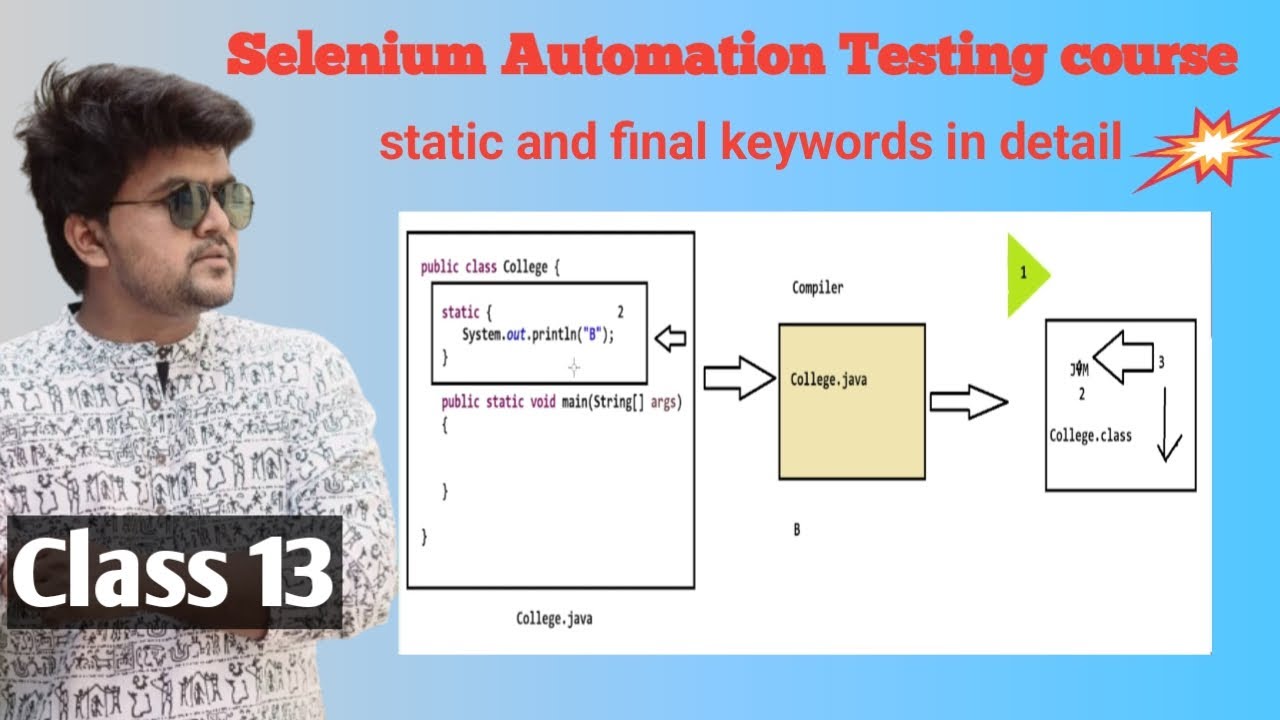
Static blocks (used for static initialization):
===================================
Static blocks are recognized and executed at the time of loading the byte code to the memory.
class MyClass {
static {
System.out.println("Static block executed once when class is loaded");
}
}
Inside a static method or block, you cannot access non-static (instance) members directly because they require an instance of the class.
static methods:-
==============
Static methods are executed at the time of calling the method using the class name or reference variable of an object.
Can we override a static method?
No, you cannot override a static method in Java — but you can hide it. This is known as method hiding, not true overriding.
Why Not Overriding?
Static methods belong to the class, not the object.
Overriding works with instance methods that are resolved at runtime (polymorphism).
Static methods are resolved at compile-time using the reference type, not the actual object.
Example: Method Hiding
=====================
class Parent {
static void display() {
System.out.println("Parent static method");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
static void display() {
System.out.println("Child static method");
}
}
Main Method:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent p = new Child();
p.display(); // Output: Parent static method ❗
}
}
Can we overload a static method?
Yes, you can overload a static method in Java.
Just like any other method, static methods can be overloaded based on different method signatures — meaning:
Different number of parameters
Different types of parameters
Different order of parameters (if types differ)
How to Work with Instance Members in Static Context?
You need to create an object:
static void myStaticMethod() {
MyClass obj = new MyClass();
System.out.println(obj.instanceVar);
}
final keyword in java:-
==================
The final keyword in Java is a non-access modifier used to indicate that something cannot be changed once it is assigned. It can be applied to:
Variables
Methods
Classes
1. Final Variables
===================
A final variable's value cannot be changed after it is assigned once.
final int x = 10;
x = 20;
You can declare a final variable without assigning it immediately, but you must assign it once before use — commonly in:
The constructor (for instance variables)
A static block (for static variables)
final int a; // allowed
a = 5; // assigned once
2. Final Methods
================
A method marked final cannot be overridden by subclasses.
class Parent {
final void show() {
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
// void show() {} // Error: Cannot override final method
}
Use Case:
Prevent critical methods from being modified in subclasses
Ensure core logic stays intact
3. Final Classes
Meaning:
A final class cannot be extended (no subclassing allowed).
final class Utility {
// helper methods
}
Important Notes
=================
Use Case Restriction
final variable Cannot be reassigned
final method Cannot be overridden
final class Cannot be extended
Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке:



















