Efficiently Convert Byte Array to 16 Bit Grayscale Image in Python
Автор: vlogize
Загружено: 2025-08-20
Просмотров: 2
Discover how to efficiently convert byte arrays to 16-bit grayscale images in Python, optimizing performance for large datasets.
---
This video is based on the question https://stackoverflow.com/q/65007614/ asked by the user 'oldbhoy' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/13659237/ ) and on the answer https://stackoverflow.com/a/65007844/ provided by the user 'tzot' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/6899/ ) at 'Stack Overflow' website. Thanks to these great users and Stackexchange community for their contributions.
Visit these links for original content and any more details, such as alternate solutions, latest updates/developments on topic, comments, revision history etc. For example, the original title of the Question was: Converting byte array to 16 bit grayscale image in Python
Also, Content (except music) licensed under CC BY-SA https://meta.stackexchange.com/help/l...
The original Question post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license, and the original Answer post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license.
If anything seems off to you, please feel free to write me at vlogize [AT] gmail [DOT] com.
---
Converting Byte Array to 16 Bit Grayscale Image in Python
When working with large image datasets, especially in non-standard formats like .Tsm, it can be challenging to efficiently convert byte arrays into usable image formats. In this guide, we’ll delve into a specific problem faced by many developers—efficiently reading and converting byte arrays into 16-bit grayscale images using Python. We’ll also explore how to optimize this process to handle larger images swiftly.
The Problem: Processing Large Image Datasets
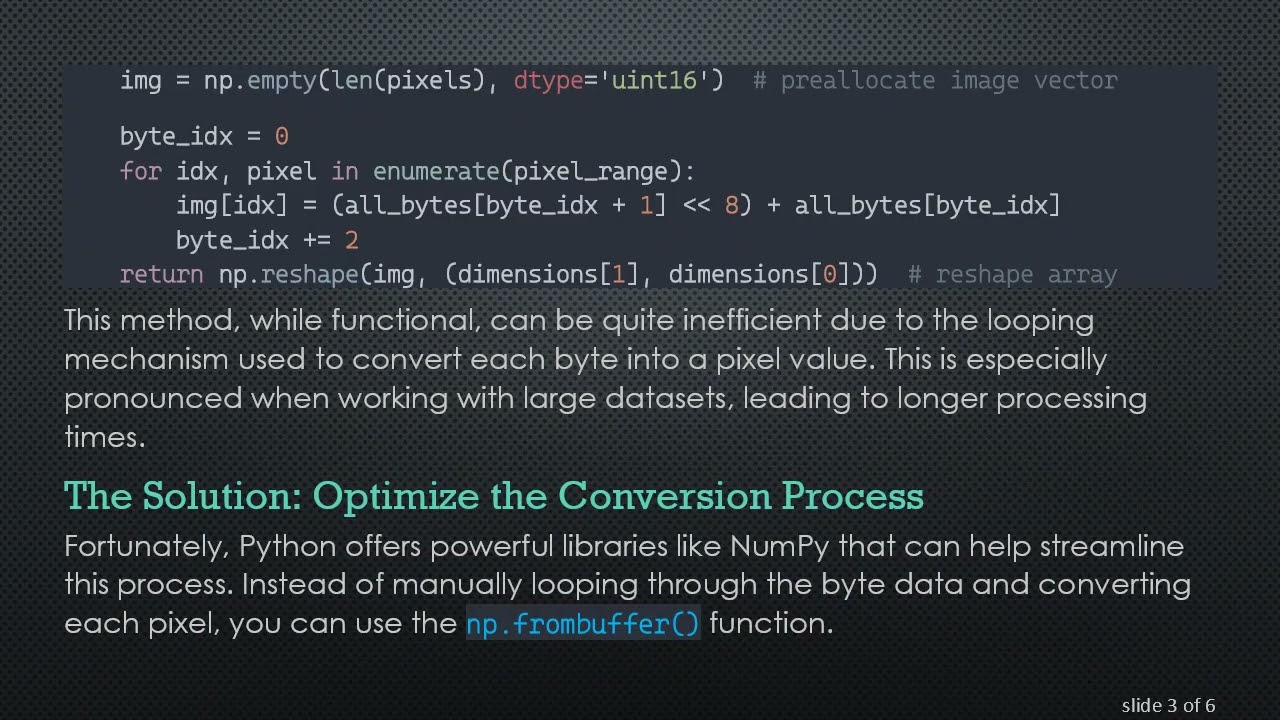
You might find yourself dealing with large images, such as 2048x2048 pixel matrices. Currently, if you are using a loop to convert a byte array into a 16-bit integer, this approach can significantly slow down your processing time. For instance, consider the code snippet you are currently using:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
This method, while functional, can be quite inefficient due to the looping mechanism used to convert each byte into a pixel value. This is especially pronounced when working with large datasets, leading to longer processing times.
The Solution: Optimize the Conversion Process
Fortunately, Python offers powerful libraries like NumPy that can help streamline this process. Instead of manually looping through the byte data and converting each pixel, you can use the np.frombuffer() function.
A More Efficient Approach
Here’s how you can optimize your code:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Example Usage
Here’s a quick example of how this function works:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
How It Works
np.frombuffer(): This function reads the byte data directly from a buffer, interpreting it as an array of 16-bit unsigned integers.
Performance: This method is much faster because it eliminates the need for Python’s looping operations and leverages NumPy’s optimized handling of large arrays.
Benefits of Using np.frombuffer()
Speed: Processes large images significantly faster by utilizing low-level operations.
Simplicity: Reduces complexity in your code, making it more readable and maintainable.
Conclusion
Utilizing NumPy’s np.frombuffer() function is a great way to optimize the conversion of byte arrays into 16-bit grayscale images. This simple change can drastically enhance the performance of image processing, especially when dealing with large datasets. If you’re working with specialized image formats like .Tsm, remember to explore the capabilities of libraries designed for efficient data handling, such as NumPy. By following these practices, you can streamline your workflow and focus more on analysis rather than data processing bottlenecks.
Happy coding!
Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке:



















