Understanding the list_add Function in Linux Kernel Linked Lists: How It Works
Автор: vlogize
Загружено: 2025-09-26
Просмотров: 3
Dive deep into the `list_add` function in the Linux kernel, unraveling how this essential component manages linked lists efficiently and effectively.
---
This video is based on the question https://stackoverflow.com/q/62943547/ asked by the user 'nZaegik' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/10029996/ ) and on the answer https://stackoverflow.com/a/62944636/ provided by the user 'alx - recommends codidact' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/6872717/ ) at 'Stack Overflow' website. Thanks to these great users and Stackexchange community for their contributions.
Visit these links for original content and any more details, such as alternate solutions, latest updates/developments on topic, comments, revision history etc. For example, the original title of the Question was: How does the list_add function for linux kernel linked lists work?
Also, Content (except music) licensed under CC BY-SA https://meta.stackexchange.com/help/l...
The original Question post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license, and the original Answer post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license.
If anything seems off to you, please feel free to write me at vlogize [AT] gmail [DOT] com.
---
Understanding the list_add Function in Linux Kernel Linked Lists
The Linux kernel uses linked lists extensively to manage various data structures. If you're delving into kernel programming or trying to understand how lists are manipulated in the Linux kernel, you might have come across the list_add function. Let's explore how this function works, focusing especially on the internal function __list_add, which is critical for adding new elements to lists.
Core Concepts of Linked Lists in the Linux Kernel
Before we dive into the specifics of the list_add function, it’s helpful to understand the essential components involved in the linked list implementation in the Linux kernel:
Structure Definition: A linked list in the kernel is typically implemented using the struct list_head which contains two pointers: next and prev.
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Head Initialization: The head of a list can be initialized using macros like LIST_HEAD_INIT and LIST_HEAD to start a new linked list.
The list_add Function Explained
The list_add function is responsible for adding a new node (represented by new) to the list immediately after the specified head. The implementation looks like this:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Breaking Down list_add
Parameters:
new: This parameter is the new element you want to add to the list.
head: The head node of the list where you want to add the new element.
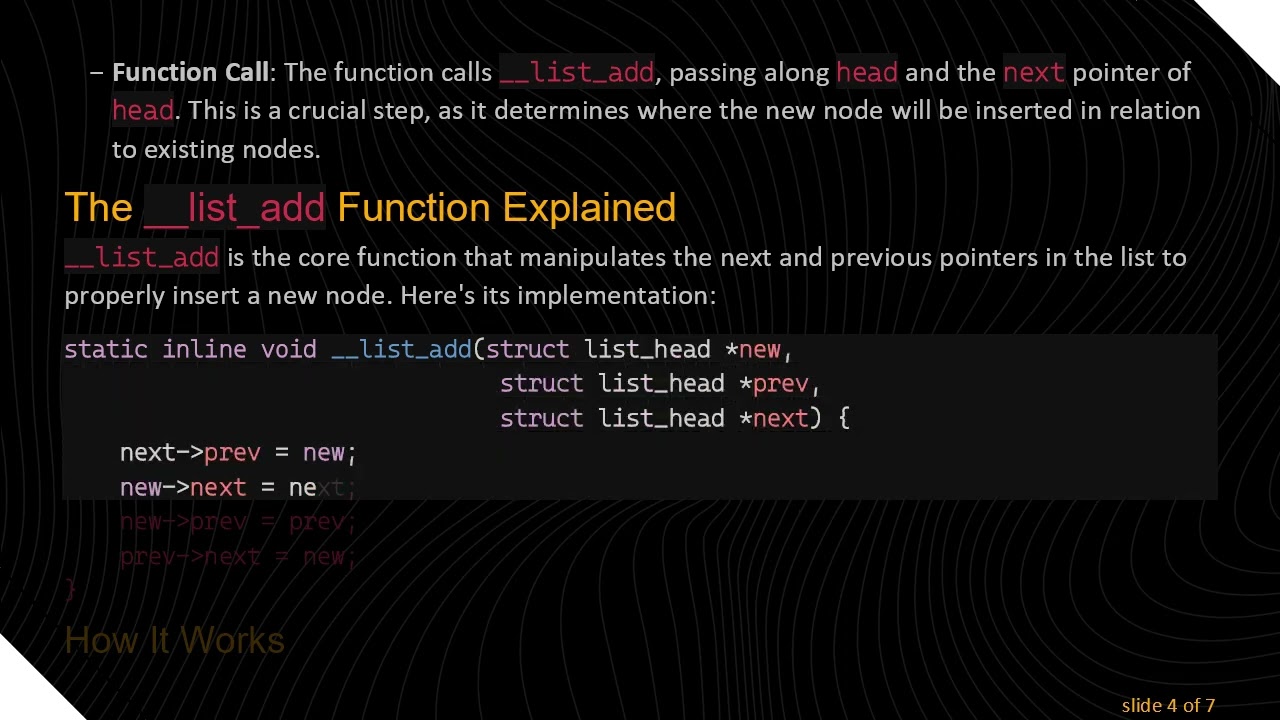
Function Call: The function calls __list_add, passing along head and the next pointer of head. This is a crucial step, as it determines where the new node will be inserted in relation to existing nodes.
The __list_add Function Explained
__list_add is the core function that manipulates the next and previous pointers in the list to properly insert a new node. Here's its implementation:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
How It Works
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of what happens when you call __list_add:
Adjust Previous Pointer: next->prev = new; - This sets the previous pointer of the node that is currently next to the head to point to the new node.
Set Next Pointer for New Node: new->next = next; - The new node’s next pointer now points to the original next node (which is currently before the new node).
Set Previous Pointer for New Node: new->prev = prev; - The new node’s prev pointer now indicates that the previous node is the head.
Update Next Pointer of Previous Node: prev->next = new; - Finally, the original head’s next pointer must be updated to point to the new node.
Visualizing the Example
Let’s consider a scenario where you already have two members in your list (_3 and _5), and you want to add a new member, _4, between them.
Start with nodes _3 and _5.
When you call list_add(_4, _3), it translates into __list_add(_4, _3, _5).
The adjustments will be as follows:
[[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]]
Conclusion
The list_add function, through its internal mechanism __list_add, efficiently manages the insertion of nodes in linked lists used within the Linux kernel. By understanding the relationship between nodes and how pointers are manipulated, programmers can leverage linked lists for dynamic data management effectively.
Now, whether you are working on kernel development or simply enhancing your knowledge, grasping how linked lists function at this level will be immensely beneficial.
If you have any questions or would like to dive deeper into another topic related to the Linux Kernel, feel free to reach out!
Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке:



















