C4 Pathway Carbon Fixation
Автор: Hussain Biology
Загружено: 2019-03-25
Просмотров: 177244
C3 Cycle : • Photosynthesis - Calvin Cycle
Photorespiration : • Photorespiration Pathway
In this video we have discussed the C4 Pathway in Plants which avoids the Photorespiration pathway in plants .
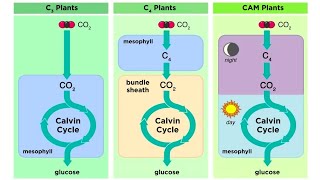
C4 carbon fixation or the Hatch–Slack pathway is a photosynthetic process in some plants. It is the first step in extracting carbon from carbon dioxide to be able to use it in sugar and other biomolecules. It is one of three known processes for carbon fixation. "C4" refers to the four-carbon molecule that is the first product of this type of carbon fixation.
C4 fixation is an elaboration of the more common C3 carbon fixation and is believed to have evolved more recently. C4 overcomes the tendency of the enzyme RuBisCO to wastefully fix oxygen rather than carbon dioxide in the process of photorespiration. This is achieved by ensuring that RuBisCO works in an environment where there is a lot of carbon dioxide and very little oxygen. CO
2 is shuttled via malate or aspartate from mesophyll cells to bundle-sheath cells. In these bundle-sheath cells CO
2 is released by decarboxylation of the malate. C4 plants use PEP carboxylase to capture more CO
2 in the mesophyll cells. PEP carboxylase (three carbons) binds to CO
2 to make oxaloacetic acid (OAA). OAA then makes malate (four carbons). Malate enters bundle sheath cells and releases the CO
2. These additional steps, however, require more energy in the form of ATP. Using this extra energy, C4 plants are able to more efficiently fix carbon in drought, high temperatures, and limitations of nitrogen or CO
2. Since the more common C3 pathway does not require this extra energy, it is more efficient in the other conditions.
In C3 plants, the first step in the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis involves the fixation of CO
2 by the enzyme RuBisCO into 3-phosphoglycerate. However, due to the dual carboxylase and oxygenase activity of RuBisCo, some part of the substrate is oxidized rather than carboxylated, resulting in loss of substrate and consumption of energy, in what is known as photorespiration.
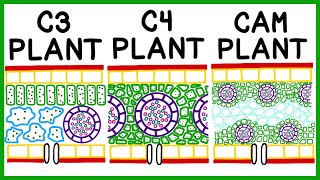
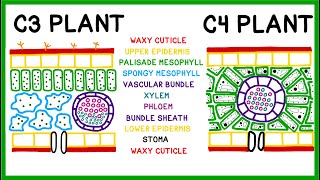
In order to bypass the photorespiration pathway, C4 plants have developed a mechanism to efficiently deliver CO
2 to the RuBisCO enzyme. They use their specific leaf anatomy where chloroplasts exist not only in the mesophyll cells in the outer part of their leaves but in the bundle sheath cells as well. Instead of direct fixation to RuBisCO in the Calvin cycle, CO
2 is incorporated into a four-carbon organic acid, which has the ability to regenerate CO
2 in the chloroplasts of the bundle sheath cells. Bundle sheath cells can then use this CO
2 to generate carbohydrates by the conventional C3 pathway.

Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке: