Heart valves and their functions
Автор: Raptor-27
Загружено: 2024-06-14
Просмотров: 21
v About this view:
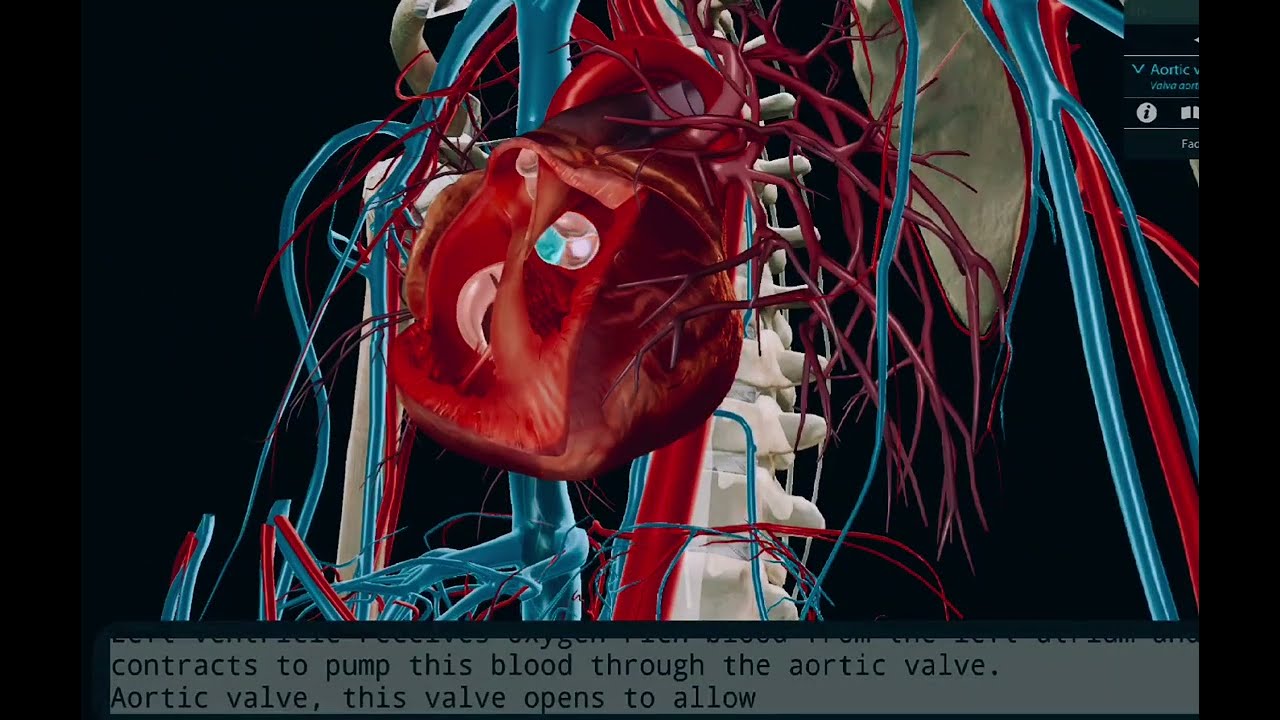
The heart's interior comprises two upper chambers, the atria, and two lower chambers, the ventricles. Atrioventricular (AV) valves between the atria and ventricles, and semilunar valves between the ventricles and the arteries outside the heart, regulate the direction of blood flow,
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation via the vena cavae. The right ventricle receives that blood from the atrium, then contracts to eject it through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs. Simultaneously, the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins. The left ventricle receives that blood from the atrium, then contracts to eject it through the aorta to the systemic circulation
The AV valves open to allow blood flow from the atria to the ventricles. When the ventricles contract, the AV valves close to prevent backflow. Simultaneously, ventricular contraction forces the semilunar valves open, allowing for blood ejection. When contraction finishes, the semilunar valves shut to prevent backflow from the arteries.
Right ventricle Ventriculus dexter
v About this view: The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation via the superior and inferior vena cavae. The right ventricle receives that blood from the atrium, then contracts to eject it through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs for gas exchange
Lett ventricle Ventriculus sinister
v About this view: The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins. The left ventricle receives that blood from the atrium, then contracts to eject it through the aorta to the systemic circulation.,
V Atrioventricular valves Valvae atrioventriculares
v About this view: The two atrioventricular (AV) valves are the tricuspid valve, between the right atrium and right ventricle, and the mitral valve, between the left atrium and left ventricle The cusps of both valves are membranous folds, connected by fibrous tendons (the chordae tendineae) to papillary muscles that project from the ventricle walls.
When the atria are full and the ventricles relax, the AV valves are pushed open to allow blood flow. When the ventricles contract, the increased ventricular pressure pushes the AV valves closed, and the papillary muscles pull down on the chordae tendineae. This stops the valve cusps from blowing back into the atria during contraction, and so prevents backflow (regurgitation) of blood.
V
Pulmonary valve Valva trunci pulmonalis
v About this view: The two semilunar valves are the pulmonary valve, between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk, and the aortic valve, between the left ventricle and the aorta.
Ventricular contraction forces the semilunar valves open, allowing for blood ejection. When contraction finishes, increased pressure in the arteries pushes the semilunar valves shut, preventing backflow (regurgitation) of blood.
#function
#heart
#valves
#bloodcirculation
#anatomy
Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке:



















