The Playbook for Primary Aldosteronism: Insights from the New 2025 Guidelines
Автор: Endocrinology India
Загружено: 2025-08-11
Просмотров: 567
Now you can ask questions to the guidelines using our Google Notebook access: https://notebooklm.google.com/noteboo...
Reference:
Adler GK, Stowasser M, Correa RR, Khan N, Kline G, McGowan MJ, et al. Primary Aldosteronism: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Jul 14. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaf284
---
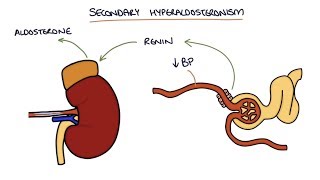
Clarification on Medication Effects on Primary Aldosteronism Screening:
Medications can significantly interfere with Primary Aldosteronism (PA) screening results by affecting aldosterone and renin levels, potentially leading to false-positive or false-negative diagnoses. To ensure accurate interpretation of screening tests (aldosterone and renin measurements, and the aldosterone to renin ratio [ARR]), managing these medications is crucial, depending on individual safety and feasibility.
Here's a detailed breakdown of medication interference and withdrawal strategies:
I. Medications and Their Effects on Renin and Aldosterone:
• Medications that Lower Renin:
◦ Beta-adrenergic blockers.
◦ Centrally acting alpha2-agonists (e.g., clonidine, alpha-methyldopa).
◦ NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs).
◦ Combined estrogen and progesterone-containing Oral Contraceptive Pills (OCPs) and Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) decrease Direct Renin Concentration (DRC).
• Medications that Raise Renin:
◦ Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists (MRAs).
◦ Diuretics, including Epithelial Sodium-Channel (ENaC) inhibitors (e.g., amiloride, triamterene).
◦ Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs).
◦ Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.
◦ Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors.
◦ Combined estrogen and progesterone-containing OCPs and HRT increase Plasma Renin Activity (PRA).
◦ Drospirenone (in OCPs) blocks the MR, which increases PRA and DRC.
• Medications that Lower Aldosterone:
◦ ARBs.
◦ ACE inhibitors.
◦ Beta-adrenergic blockers.
◦ Centrally acting alpha2-agonists (e.g., clonidine, alpha-methyldopa).
• Medications that Raise Aldosterone:
◦ Diuretics (including MRAs), by promoting natriuresis, can induce a rise in aldosterone secondary to a rise in renin/angiotensin II. However, this might be mitigated by hypokalemia with thiazide or loop diuretics.
◦ MRAs.
◦ Combined estrogen and progesterone-containing OCPs and HRT.
◦ Drospirenone.
II. Strategies for Managing Interfering Medications During PA Screening:
The Guideline Development Panel (GDP) outlined several strategies, acknowledging that the accuracy of testing improves with medication withdrawal, but also offering pragmatic approaches.
• No Medication Withdrawal Strategy:
◦ Medications: None withdrawn.
◦ Interpretation of Negative Screen: Possible false negative, especially if there is a moderate to high pretest probability for PA. In such cases, the screen should be repeated on a different day using a minimal- or full-medication withdrawal strategy.
◦ Interpretation of Positive Screen: Possible false positive if the individual is taking beta-adrenergic blockers or centrally acting alpha2-agonists (clonidine, alpha-methyldopa). In this situation, the screen should be repeated after withdrawing these medications.
• Minimal Medication Withdrawal Strategy:
◦ Medications to Withdraw: MRAs and ENaC inhibitors (amiloride, triamterene).
◦ Timeline of Withdrawal: 4 weeks before testing.
◦ Replacement Antihypertensive Agents (if needed): Hydralazine, alpha1-adrenergic blockers, non-dihydropyridine Calcium-Channel Blockers (CCBs), Moxonidine. Ideally, hydralazine should be administered with a negative chronotropic agent like verapamil slow release to avoid reflex tachycardia.
◦ Interpretation of Negative Screen: Possible false negative if moderate to high pretest probability. Repeat screen on a different day with full withdrawal strategy. If pretest probability is low, then likely a true negative.
◦ Interpretation of Positive Screen: Likely true positive; proceed to the management algorithm (Figure 2).
◦ Additionally, for this strategy, or the 'No Medication Withdrawal' strategy, consider withdrawing: Beta-adrenergic blockers and centrally acting alpha2-agonists (clonidine, alpha-methyldopa) for 2 weeks before testing if safe and feasible. Be aware of potential false positives induced by beta-adrenergic blockers when aldosterone is 10-15 ng/dL (277-416 pmol/L) by immunoassay or 7.5-10 ng/dL (208-277 pmol/L) by LC-MS/MS; if aldosterone is above these concentrations, PA is likely despite being on these blockers.

Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке: