From NAND To GPT 04: Memory
Автор: NAND to GPT
Загружено: 2026-01-15
Просмотров: 12
All our circuits so far are stateless - outputs depend only on current inputs. But computation requires remembering intermediate results. This episode introduces feedback loops and shows how cross-coupled gates create bistable circuits that hold their state. We build from the basic SR latch to D flip-flops, registers, and RAM.
Key Concepts
Feedback Loop - Connecting a gate's output back to its input. This circular path allows circuits to maintain state - the output reinforces itself through the loop.
SR Latch - Two cross-coupled NAND gates. S (Set) makes Q=1. R (Reset) makes Q=0. When both inputs are inactive, the latch holds its previous state. The simplest memory circuit.
Clock Signal - A regular oscillation that synchronizes all state changes. Think of it as the circuit's heartbeat. Data is captured only at specific moments (clock edges), making behavior predictable.
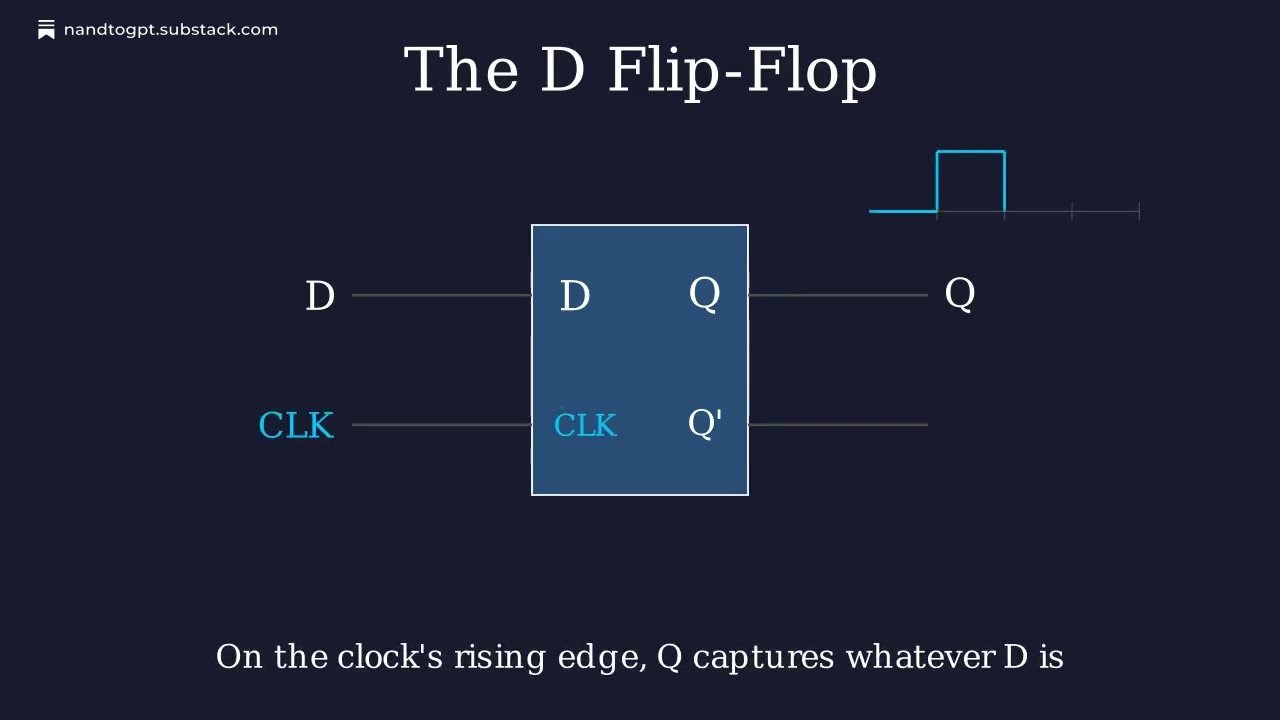
D Flip-Flop - A latch enhanced with clock control. Captures the D (data) input only on the rising edge of the clock. At all other times, the output holds steady regardless of input changes.
Register - Multiple flip-flops sharing the same clock. A 4-bit register stores a 4-bit number. Registers are the CPU's fast, close-at-hand working memory.
RAM (Random Access Memory) - A large array of memory cells with address-based selection. A decoder converts address bits into row/column selection, enabling read/write access to any location.
Why It Matters
Memory transforms what circuits can do. Without memory, circuits are pure functions - same inputs always produce same outputs. With memory, circuits become state machines that can sequence through operations, count events, and follow programs. The combination of ALU (computation) + Memory (state) is the foundation of every computer.
Signal Conventions Used
Active-low inputs - SR latch inputs are active when LOW (0), not HIGH (1)
Rising edge - Transition from 0 to 1 on the clock signal
Hold state - When both SR latch inputs are HIGH (inactive), output maintains previous value
Further Reading
Flip-flop (electronics) - History and variants - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flip-fl...
Latch (electronics) - Level-sensitive vs edge-triggered - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flip-fl...
Clock signal - Synchronization fundamentals - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clock_s...
Register (computing) - CPU registers explained - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Process...
Random-access memory - RAM architecture and types - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random-...
Memory hierarchy - Registers, cache, and main memory - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Memory_...
https://nandtogpt.substack.com/p/from...
Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке:



















