Non Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs | Mechanism of Action | Uses | Pharmacokinetic (Part II)
Автор: Pharma Inn's Tuition
Загружено: 2021-08-21
Просмотров: 2742
Part I of NSAIDs - • Mechanism of Pain, Inflammation, fever | N...
Time Stamps-
00:09 Classification of non selective NSAIDs
06:00 Classification of Preferential COX 2 Inhibitors
07:11 Classification of selective COX 2 Inhibitors
08:40 Classification of Analgesic Antipyretic and Anti inflammatory Drugs.
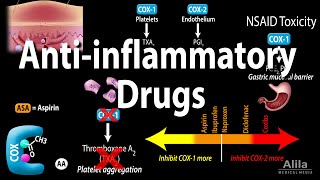
Prostaglandins are a family of chemicals that are produced by the cells of the body and have several important functions. They promote inflammation that is necessary for healing, but also results in pain, and fever; support the blood clotting function of platelets; and protect the lining of the stomach from the damaging effects of acid.
Prostaglandins are produced within the body's cells by the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX). There are two COX enzymes, COX-1 and COX-2. Both enzymes produce prostaglandins that promote inflammation, pain, and fever. However, only COX-1 produces prostaglandins that support platelets and protect the stomach. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) block the COX enzymes and reduce prostaglandins throughout the body. As a consequence, ongoing inflammation, pain, and fever are reduced. Since the prostaglandins that protect the stomach and support platelets and blood clotting also are reduced, NSAIDs can cause ulcers in the stomach and promote bleeding.
#Phrmacology
#pharmacy
#NSAIDs
#Mechnism
#Hospial_and_clinical_pharmcy
#Indu_tewari
#Pharmainnstuition
#Health_Eucation
#Community_pharmacy
#Clinical_pharmacy
#Medical_science
#EEG
#Blood_test
#Diagnosis of #Sleeping #Disorders
#Medical #Treatment of Sleeping Disorders

Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке:









![Pharmacology of NSAIDs [COX-1and COX-2 physiology, Side effects]](https://ricktube.ru/thumbnail/YFztkYS1DnU/mqdefault.jpg)








