Basic Trigonometry Concept | Trigonometric Ratios | Trigonometry formula | Sin cos tan | INPS Class
Автор: INPS CLASSES
Загружено: 2019-03-11
Просмотров: 3322
Basic Trigonometry Concept | Trigonometric Ratios | Trigonometry formula | Sin cos tan | Trigonometric Identities | INPS Classes
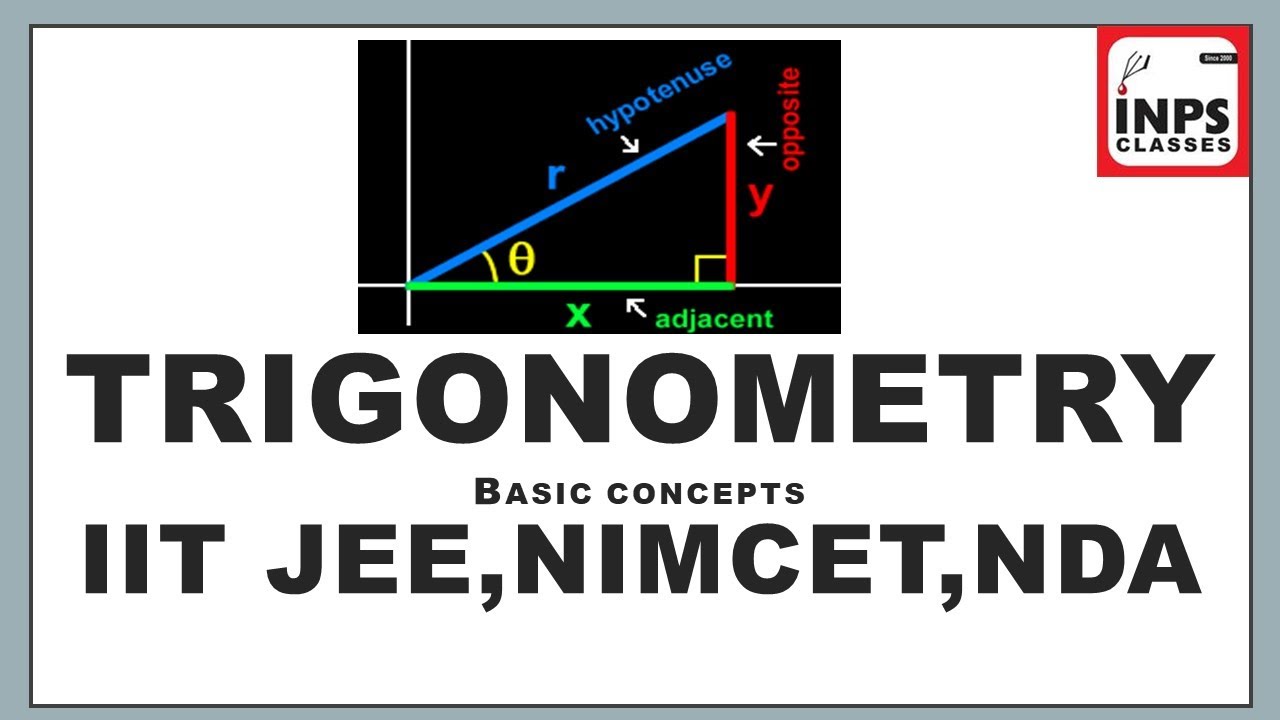
Very Important Chapter of Basic mathematics.
Useful for all students Appearing in NIMCET, IIT JEE, NDA, ISC and CBSE Board exams.
Trigonometric Identity
A trigonometric equation that holds good for every angle is called a trigonometric identity. Some of the important trigonometric identities are listed below:
Angle-Sum and Difference Identities
sin (α + β) = sin (α)cos (β) + cos (α)sin (β)
sin (α – β) = sin (α)cos (β) – cos (α)sin (β)
cos (α + β) = cos (α)cos (β) – sin (α)sin (β)
cos (α – β) = cos (α)cos (β) + sin (α)sin (β)
tan (A + B) = (tan A + tan B)/(1 - tan A tan B)
tan (A - B) = (tan A - tan B)/(1 + tan A tan B)
cot (A + B) = (cot A cot B - 1)/(cot A + cot B)
cot (A - B) = (cot A cot B + 1)/(cot B - cot A)
Multiple Angle Identities
sin 2A = 2 sin A cos A = 2 tan A/ (1 + tan2A)
cos 2A = (1 - tan2A)/(1 + tan2A)
tan 2A = 2 tan A/(1 - tan2A)
sin 3A = 3 sin A – 4 sin3A
sin 3A = 4 sin (60° - A) sin A sin (60° + A)
cos 3A = 4 cos3A – 3 cos A
cos 3A = 4 cos (60° - A) cos A cos (60° + A)
tan 3A = tan (60° - A) tan A tan (60° + A)
tan 3A = (3tan A – tan3A)/(1 - 3tan2A) (provided A ≠ nπ + π/6)
Half-Angle Identities
sin A/2 = ± √(1 - cos A)/ 2
cos A/2 = ± √(1 + cos A)/ 2
tan A/2 = ± √(1 - cos A)/(1 + cos A)
Other Important Formulae
sin A + sin B = 2 sin (A+B)/2 . cos (A-B)/2
sin A - sin B = 2 cos (A+B)/2 . sin (A-B)/2
cos A + cos B = 2 cos (A+B)/2 . cos (A-B)/2
cos A - cos B = 2 sin (A+B)/2 . sin (B-A)/2
tan A ± tan B = sin (A ± B)/ cos A cos B, provided A ≠ nπ + π/2, B ≠ mπ
cot A ± cot B = sin (B ± A)/ sin A sin B, provided A ≠ nπ, B ≠ mπ+ π/2
1 + tan A tan B = cos (A-B)/ cos A cos B
1 - tan A tan B = cos (A+B)/ cos A cos B
Product Identities
2 sin A cos B = sin (A+B) + sin (A-B)
2 cos A sin B = sin (A+B) - sin (A-B)
2 cos A cos B = cos (A+B) + cos (A-B)
2 sin A sin B = cos (A-B) – cos (A+B)
Trigonometric Equations
The equations involving trigonometric functions of unknown angles are known as trigonometric equations. For e.g. sin2 A + sin A = 2 is a trigonometric equation.
Period of a Function: A function f(x) is said to be periodic if there exists a T positive such that f(x+T) = f(x) for all x in the domain. If ‘T’ is the smallest positive real number satisfying this condition, then it is called the period of f(x).
Graphical representation of sin x
As shown above, sin x is periodic with period 2π, i.e. the graph repeats itself after every interval of 2π.
These concepts have been discussed in detail in the coming sections. For more, please refer to the following pages.
Illustration: In any triangle, prove that
cot A/2 + cot B/2 + cot C/2 = cot A/2 cot B/2 cot C/2
Solution: We know that if A, B and C are angles of a triangle, then A + B + C = π.
This means that A/2 + B/2 + C/2 = π/2.
or, we have A/2 + B/2 = π/2 - C/2.
Then, cot (A/2 + B/2) = cot (π/2 - C/2)
Using the identity cot (A + B) = (cot A cot B - 1)/(cot A + cot B), we have
[cot A/2.cot B/2 – 1]/ [cot (A/2 + B/2)] = tan C/2
This gives cot A/2 .cot B/2. cot C/2 - cot C/2 = cot A/2 + cot B/2
Hence, we have cot A/2 + cot B/2 + cot C/2 = cot A/2 .cot B/2. cot C/2
Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке:



















