FEA Isoparametric Quadrilaterals Part 1: Jacobian matrix and natural coordinates
Автор: Michael Sevier
Загружено: 2024-07-25
Просмотров: 2053
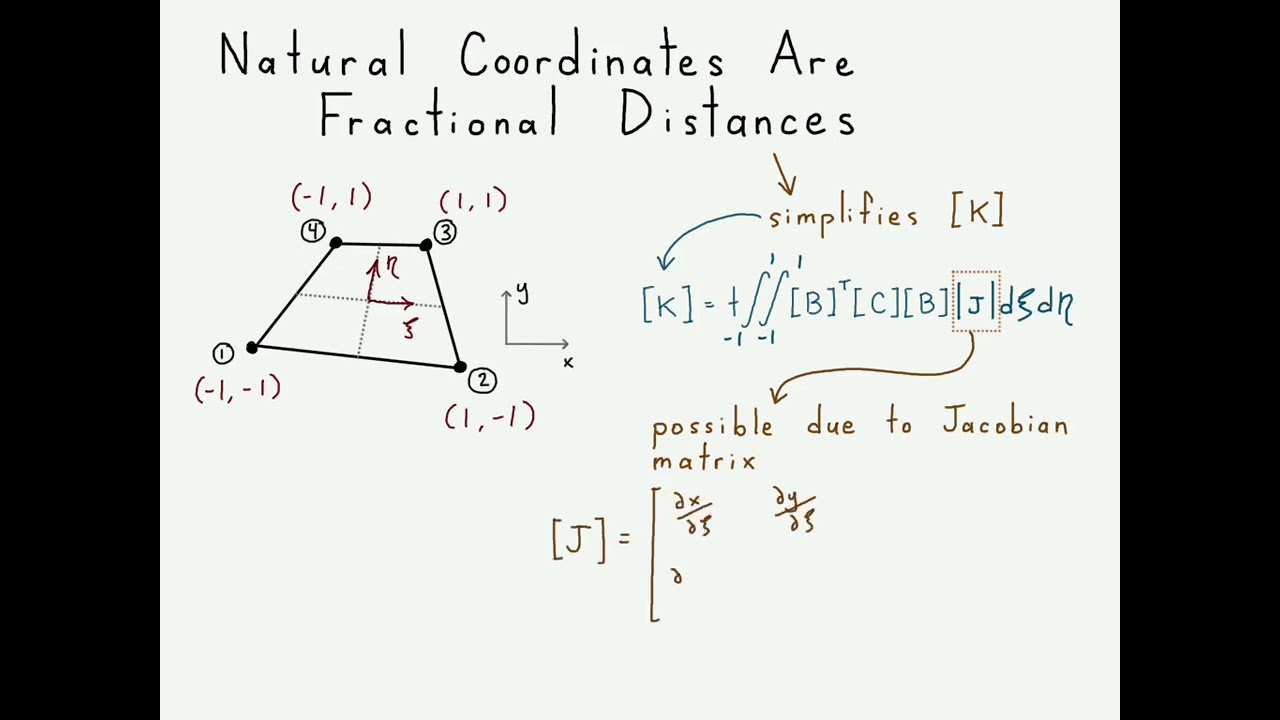
This video shows the first steps in how to develop the stiffness matrix for linear 4-node isoparametric quadrilateral elements in finite element analysis (FEA). The form of the stiffness matrix is very similar to that for constant strain triangles. There are a couple big differences however. First, the shape functions are based on fractional distances throughout the element instead of global x, y locations. These fractional measurements from the center to any edge are called "natural coordinates." The Jacobian matrix is used to map between natural coordinates and global coordinates. The second big difference is that quadrilateral elements have a shear flexibility term which allows for stresses and strains to vary throughout the element. However, this also means that the integrand of the stiffness matrix equation is not constant and thus integration is required.
0:00 Introduction and basic concepts for the linear isoparametric quadrilateral element
2:01 Description of shear flexibility term and why strain and stress can vary in the element as a result
4:05 Description of natural coordinates and their purpose
6:10 Description of Jacobian matrix and its purpose
7:38 Description of shape functions
9:43 Use shape functions to evaluate Jacobian matrix in terms of natural coordinates and nodal x, y positions
12:02 The Jacobian ratio - How the Jacobian matrix is used to determine element quality
13:44 Reflection questions
Suggested answers to reflection questions
1.) Stress and strain can vary linearly within 4-node quadrilateral elements and cannot vary in 3-node constant strain triangle (CST) elements. This is why quadrilateral elements converge more quickly
2.) The purpose of natural coordinates is to make integration of the stiffness matrix possible by giving easy limits of integration (-1 to 1). The shape functions are much easier to define.
3.) The shape functions for the isoparametric quadrilateral element must be 1.0 at their corresponding node (e.g., node 1 for shape function 1, N1) and zero at all other nodes. They also must have the same form as the possible methods of motion (i.e., the displacement function). Then one simply maps the boundary condition requirements (i.e., where the shape function is one and zero) to the form of the function. For these elements, it is much easier to use natural coordinates (same for every isoparametric element) than physical x, y coordinates (different for every isoparametric element).
4.) The purpose of the Jacobian matrix is to map between the natural coordinates of the isoparametric element and the physical x, y location of nodes in the element.
Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео mp4
-
Информация по загрузке:



















